Astrology

Astrology
The symbolic language of the stars – reflecting cosmic rhythms in human life
Definition:
Astrology (from Greek astron = star, logos = study or word) is a symbolic and spiritual system that interprets the movements and positions of celestial bodies—such as the Sun, Moon, and planets—as reflections of both personal inner states and collective cycles. Rooted in the hermetic principle:
“As above, so below; as within, so without,”
astrology views the macrocosm (universe) and the microcosm (human being) as interconnected.
Astrology is practiced across cultures and centuries in diverse forms, including Western astrology, Vedic (Jyotish) astrology, and Chinese astrology.
🜁 Core Principles of Astrology
| Principle | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Cosmic Resonance | Planetary cycles mirror events and psychological themes on Earth |
| Birth Moment as Blueprint | The natal chart reflects a soul’s archetypal potential and life themes |
| Archetypes and Symbols | Planets, signs, and houses represent universal forces and inner patterns |
| Free Will and Timing | Astrology does not predict fixed outcomes but offers insight and guidance for conscious choice |
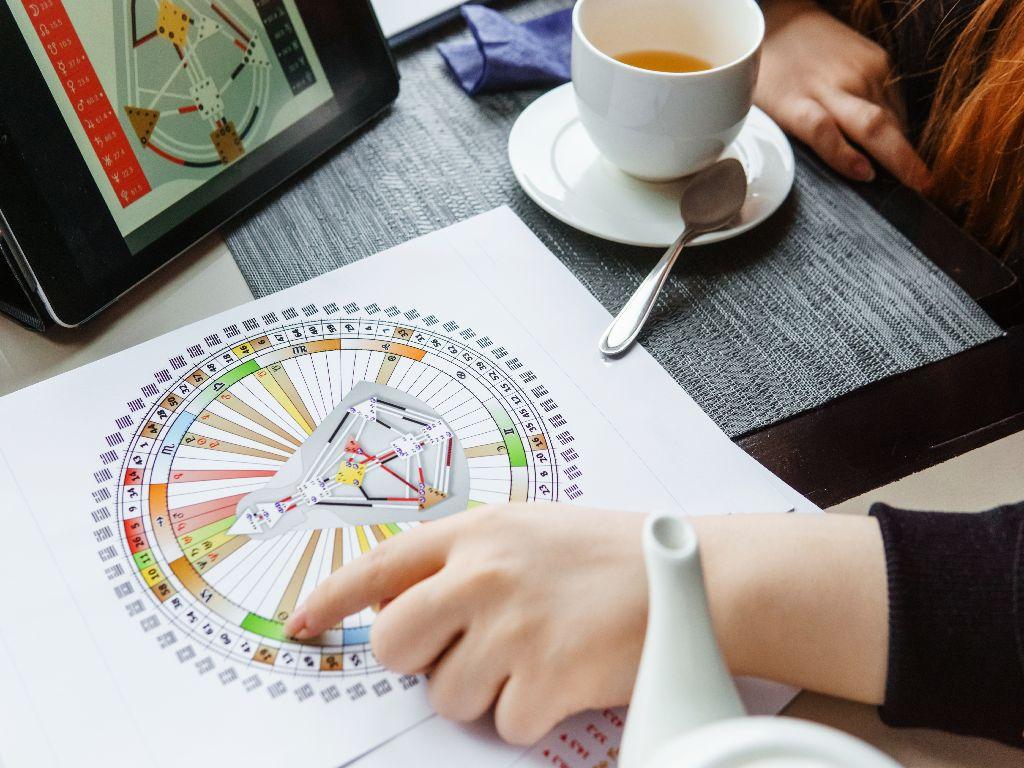
🜂 Key Components of a Natal Chart
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Zodiac Signs (e.g., Aries, Libra) | Describe qualities and modes of expression |
| Planets (e.g., Mars, Venus) | Represent psychological functions and energetic drives |
| Houses (1st–12th) | Show life areas where planetary energies manifest |
| Aspects (e.g., trine, square) | Indicate relationships between planets—supportive or challenging |
🜃 Astrology as a Spiritual Tool
-
Self-knowledge: A natal chart reveals patterns, strengths, and soul lessons
-
Timing & Life Cycles: Planetary transits and progressions help navigate transitions and spiritual growth
-
Karmic and Evolutionary Insight: Some traditions see the chart as a map of reincarnational themes
-
Ritual Alignment: Astrological timing is often used for new moon rituals, seasonal ceremonies, or chakra attunement
🜄 Forms and Systems of Astrology
| System | Focus |
|---|---|
| Western Astrology | Psychological, symbolic, uses tropical zodiac |
| Vedic (Jyotish) | Sidereal system; karmic, dharmic, and predictive |
| Chinese Astrology | Based on lunar years, five elements, yin-yang dynamics |
| Uranian / Hamburg School | Modern method with hypothetical planets and points |
| Astrocartography | Links astrological influences with geography and place |
🜅 Astrology Through the Ages
-
Ancient Times: Integrated into medicine, politics, and sacred rites
-
Middle Ages: Used by monks and scholars; later suppressed by religious institutions
-
Enlightenment Era: Dismissed as superstition
-
Modern Era: Reclaimed through psychological astrology (e.g., C.G. Jung), soul-based guidance, and personal empowerment
Related Terms:
Horoscope, Zodiac, Transits, Karma, Archetypes, Planetary Influence, Natal Chart, Soul Journey, Cosmic Cycles, Self-Inquiry