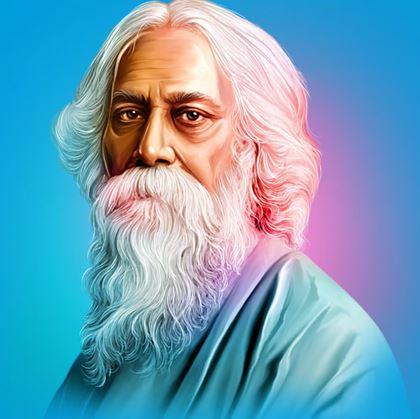
Rabindranath Tagore (1861–1941) was a renowned Indian poet, philosopher, musician, and artist, best known for his contributions to literature, music, and the arts. He is celebrated for his profound impact on Bengali literature and for being the first non-European to win the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913. His works have a lasting legacy both in India and worldwide.
Key Aspects of Rabindranath Tagore’s Life and Work:
-
Early Life:
-
Tagore was born in Calcutta (now Kolkata) into a prominent Bengali family. His family was part of the Brahmo Samaj, a reformist Hindu movement that emphasized rationality and social progress.
-
He was a child prodigy, writing poems at a very young age, and was largely self-educated. His family nurtured his artistic and intellectual pursuits.
-
-
Literary Contributions:
-
Poetry: Tagore is best known for his poetry, which is characterized by its lyricism, deep philosophical insights, and exploration of themes like spirituality, nature, love, and human connection. His Gitanjali ("Song Offerings"), a collection of poems, won him the Nobel Prize in Literature. These poems are considered a spiritual and literary masterpiece and showcase his deep connection to the divine and humanism.
-
Novels and Short Stories: In addition to poetry, Tagore wrote several novels and short stories, often focusing on the lives of ordinary people, social issues, and the changing dynamics of Indian society during the British colonial period. Notable works include "Gora", "Chokher Bali", and "Shesher Kobita".
-
Essays and Philosophy: Tagore was also a prominent philosopher and thinker. He wrote extensively on topics like education, nationalism, spirituality, and the importance of human freedom. His thoughts on "universalism" and "humanism" were groundbreaking, advocating for the breaking down of national and cultural boundaries.
-
-
Tagore’s Views on Education:
-
Tagore was deeply critical of the traditional education system in India, which he felt was rigid and colonial in nature. He believed education should be holistic and should nurture creativity, free thought, and emotional intelligence.
-
He founded the Visva-Bharati University in Santiniketan (Bengal), which aimed to provide a unique form of education, blending Indian tradition with global perspectives.
-
-
Tagore as a Musician and Artist:
-
Tagore was not only a poet and writer but also a composer of over 2,000 songs, which are collectively known as Rabindra Sangeet. His songs are a cornerstone of Bengali culture and are still immensely popular today. They encompass a variety of themes, from love and nature to spirituality and nationalism.
-
He also painted, and his visual artwork—though not as well known—was innovative, reflecting his unique artistic sensibilities.
-
-
Tagore and Indian Nationalism:
-
Tagore was an advocate for Indian independence but was critical of some aspects of the independence movement, particularly the violent forms of nationalism. He believed in universal humanism and a world beyond national boundaries.
-
He famously gave up his knighthood in 1919 as a protest against the Jallianwala Bagh massacre, where British troops killed hundreds of unarmed Indian civilians.
-
-
Global Impact and Legacy:
-
Tagore’s influence extended beyond India. He traveled extensively across Europe and the world, meeting with prominent thinkers and artists of the time, including Albert Einstein, with whom he had discussions on science and philosophy.
-
He translated his own works into English, bringing them to a global audience and spreading his ideas of peace, spirituality, and social harmony. He continues to be a symbol of cultural fusion, bridging Eastern and Western thought.
-
Famous Works of Rabindranath Tagore:
-
Gitanjali (Song Offerings) – His most famous work, a collection of poems that explore themes of devotion, spirituality, and the divine.
-
Rabindra Sangeet – His collection of songs that continues to influence Bengali and Indian music.
-
Gora – A novel dealing with themes of nationalism, religious identity, and personal belief.
-
Chokher Bali – A novella that addresses themes of love, betrayal, and human emotion.
-
Shesher Kobita (The Last Poem) – A famous novel about love, self-expression, and emotional conflict.
Conclusion:
Rabindranath Tagore is considered one of the greatest cultural figures in Indian history. His work transcended boundaries, encompassing the spiritual, intellectual, and artistic. Through his poetry, music, and philosophy, Tagore contributed immensely to modern Indian identity and continues to influence global thought on spirituality, humanity, and the arts. His ability to intertwine Eastern mysticism with Western ideas made him a truly universal figure.